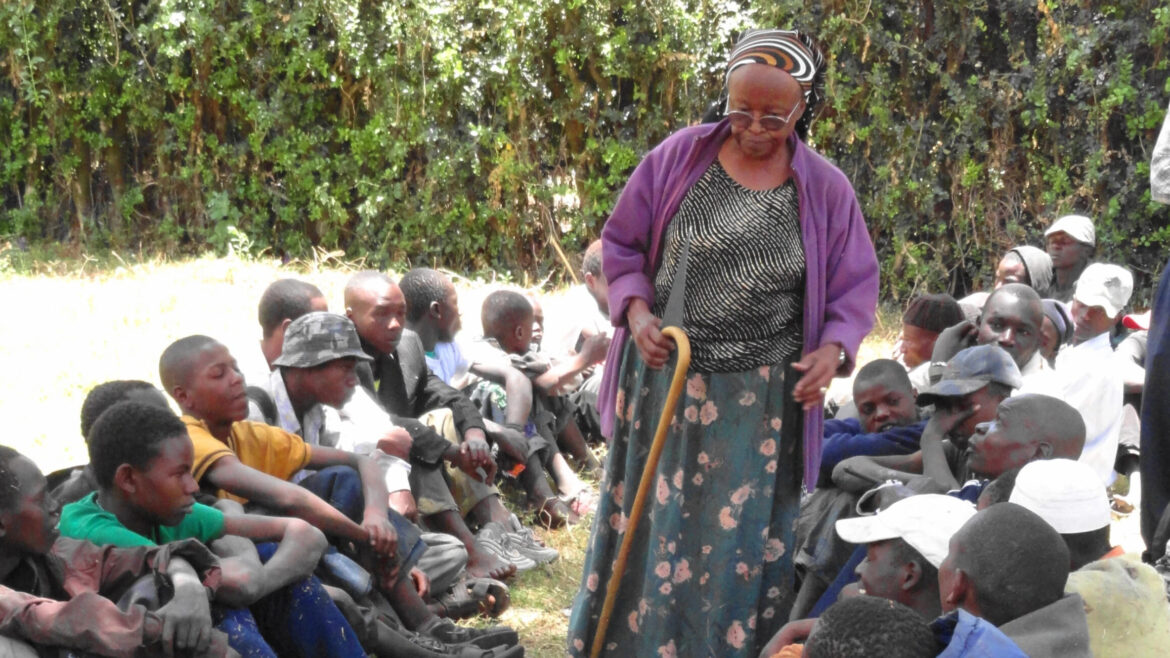
Urban migration in Kenya refers to the movement of people from rural areas to cities in search of better economic opportunities, education, and essential services. This migration pattern has played a crucial role in shaping the country’s urban growth, influencing housing, employment, and infrastructure development in major cities like Nairobi and Mombasa.
Historical Context of Migration in Kenya
The history of urban migration in Kenya dates back to the colonial era when cities like Nairobi and Mombasa emerged as administrative and economic hubs. Labor migration from rural areas to these urban centers began then and has continued post-independence, driven by expanding opportunities in education, employment, and commerce.
Current Trends and Statistics
As of recent data, about 25% of Kenya’s population lives in urban areas, with an annual urbanization rate of 4.4%. Nairobi alone had over 4.3 million residents in 2019. A large portion of this urban growth results from urban migration in Kenya, as people relocate in search of economic opportunities.
Read more:
Drivers of Migration in Kenya
Several factors contribute to the migration from rural to urban areas in Kenya:
- Economic Opportunities: Urban centers offer more diverse employment opportunities compared to rural areas. Many migrants seek jobs in the informal sector, which, while often low-paying, are more abundant in cities.
- Education and Healthcare: Cities provide better access to educational institutions and healthcare facilities, attracting families aiming for improved services.
- Environmental Factors: Climate change and environmental degradation have adversely affected agricultural productivity in rural areas, prompting individuals, including children, to migrate to urban centers to escape climate threats.
Read more:
- Rural Out-Migration to Urban Uncertainties in Kenya
- Climate change induces child rural to urban migration in Kenya
Impacts of Urban Migration
While migration can lead to improved livelihoods for some, it also presents challenges:
- Urbanization and Housing: Rapid urbanization has led to the proliferation of informal settlements and slums in cities like Nairobi. For instance, Kibera, one of Nairobi’s largest informal settlements, has grown significantly due to rural-urban migration.
- Employment Strain: The influx of migrants often exceeds the capacity of urban economies to provide adequate formal employment, leading many to seek work in the informal sector with often inadequate pay.
- Environmental Concerns: Increased urban populations contribute to challenges such as waste management and pollution. For example, in Nairobi, only a portion of solid waste is collected, with the remainder often disposed of improperly, leading to environmental degradation.
Read more:
Policy Solutions for Migration in Kenya
Addressing the challenges of rural-urban migration requires comprehensive strategies:
- Economic Development in Rural Areas: Investing in rural infrastructure, education, and healthcare can reduce the push factors driving migration. Engaging both migrants and non-migrants in county-based initiatives can improve livelihoods and promote local economic development.
- Better Urban Planning: Implementing effective urban planning policies can accommodate growing urban populations, ensuring adequate housing, sanitation, and waste management systems.
- Employment Initiatives: Expanding job opportunities in both urban and rural areas can help manage migration patterns.
Urban migration in Kenya is shaping the country’s future. By promoting balanced regional development and effective urban policies, Kenya can create sustainable growth for both rural and urban communities.
Support Sustainable Solutions to Urban Migration in Kenya
Urban migration in Kenya continues to shape cities, but sustainable rural opportunities can help address its root causes. At Mwandani International, we empower vulnerable communities through value-added agriculture, creating jobs and economic stability to reduce the need for migration. Your support can help us expand these initiatives, providing sustainable livelihoods for single mothers, widows, and rural farmers. Donate today to be part of the solution, and help us spread awareness by sharing this article with your network!